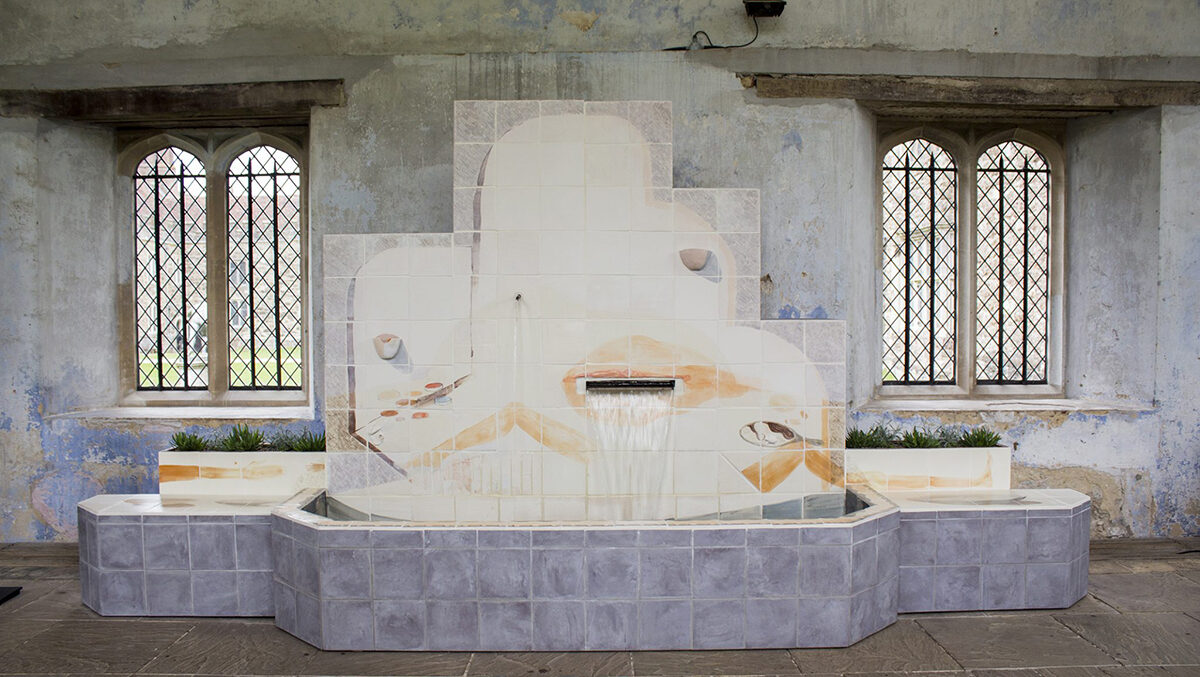

Emily Speed announced as second Artist in Residence at Energy House 2.0
Posted on 4 July 2023
We are delighted to announce that the second of two artist residencies at Energy House 2.0 has been awarded to Emily Speed by The University of Salford Art Collection, in partnership with Castlefield Gallery.
Cheshire-based Speed joins artist Mishka Henner, who was announced as the first artist-in-residence at the University’s world-leading research facility earlier this year, with the University of Salford Art Collection in partnership with Open Eye Gallery.
Speed was selected from an open call in early 2023 which received over 70 expressions of interest. As artist in residence, Speed will work closely with the Energy House 2.0 team over the next 18 months to develop new work in response to the groundbreaking research being carried out, around topics of energy efficiency, the climate crisis, net zero research, and the future of housing and homes.
Ideas around shelter and habitation lie at the core of much of Speed’s work, which spans disciplines from drawing to installation and performance. With two large environmentally-controllable chambers – able to accommodate two full-sized detached houses each and capable of simulating wind, rain, snow, solar radiation and extreme temperatures – the world-leading Energy House 2.0 facility, part-funded by the European Research Development Fund (ERDF), provides a unique opportunity to explore these themes and the future of housing.
On being selected for the residency, Speed says:
“I feel incredibly fortunate to have time and access to this fantastic facility and to be able to work alongside experts to develop research into the home, and how we might live in the future.”
Professor Richard Fitton, Energy House:
“Our artist in residence programme has grown from strength to strength in the past few years, and we are now on our 3rd residency, this scheme aims to take some of the building science work done at Energy House 2.0 and create ground breaking artworks – we see this as a positive impact to the work we do, engaging the public in ways that we simply could not have done beforehand. The quality of bids that we saw was amazing and Emily has some tough competition. We are now really eager to get Emily involved as part of the teams and see what she will achieve.”
Lindsay Taylor, Curator, University of Salford Art Collection:
“We were delighted to receive so many high quality applications by some fantastic artists. It was very hard to agree a shortlist and a finalist, however the panel all agreed that Emily’s interest in gender, the body and the domestic environment would bring a unique perspective to the work at Energy House 2.0”
Emily Speed
Known for her work examining the relationship between the body and architecture, Speed’s practice considers how a person is shaped by the buildings they have occupied and how a person occupies their own psychological space. Working in sculpture, performance, drawing and film, Speed’s work looks at the relationship between people and buildings and in particular the power dynamics at play in built space. Her work plays with scale and creates layers around the body, often hybrid forms of clothing and architecture.
Over the last few years, Speed has had solo presentations at Tate Liverpool, Tate St Ives, TRUCK, Calgary, and Fort Worth Contemporary Arts, Texas. She has been commissioned to make performances for Yorkshire Sculpture Park, Laumeier Sculpture Park (St Louis) and Edinburgh Art Festival among others and recent exhibitions include: A Woman’s Place at Knole House; Body Builders at Exeter Phoenix Gallery; and The Happenstance, Scotland + Venice at the Architecture Biennale in 2018. Emily Speed lives and works in Cheshire, UK.
Energy House 2.0
Launched in February 2022, Energy House 2.0 is a unique research facility, with two environmental chambers each able to accommodate two full sized detached houses. The research team can recreate a variety of environmental conditions – from extreme temperatures (-20˚C to +40˚C) to simulate wind, rain, snow, and solar radiation – in order to test out the latest innovations in the built environment. The £16m facility, part-funded by the European Research Development Fund (ERDF), is the largest facility of its type and plays a key role in accelerating progress towards low carbon and net zero housing design building upon the success of the original Energy House Laboratory which opened in 2012.
More news
PIECE BY PIECE at Castlefield Gallery New Art Spaces: Chester

CHAORDIC: New Radical Art Commissions Disrupting Narratives on Substance Use and Recovery

Castlefield Gallery qualifies as a 2024 Gallery Climate Coalition Active Member

Announcing our Brian Mercer Trust supported Castlefield Gallery Associates

